Introduction
Overview of HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, regardless of outside air conditions. These systems are designed to regulate temperature, control humidity, and improve indoor air quality. Choosing the right HVAC system is crucial not only for comfort but also for energy efficiency and long-term cost savings.
Whether you are considering a cooling system or a comprehensive HVAC unit, it’s important to evaluate factors like energy consumption, system longevity, and the specific demands of your local climate. An energy-efficient system not only reduces your carbon footprint but also offers significant savings on utility bills over time, making the right choice a valuable investment. Understanding how this HVAC system functions is key to making an informed decision.
The Role of Climate in HVAC Selection
The climate you live in significantly determines which type of HVAC system will best suit your needs. Different climates demand different features, whether it’s powerful heating for cold winters, effective cooling for hot summers, or humidity control for humid environments. The key differences in selecting the right system tailored to your climate can ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
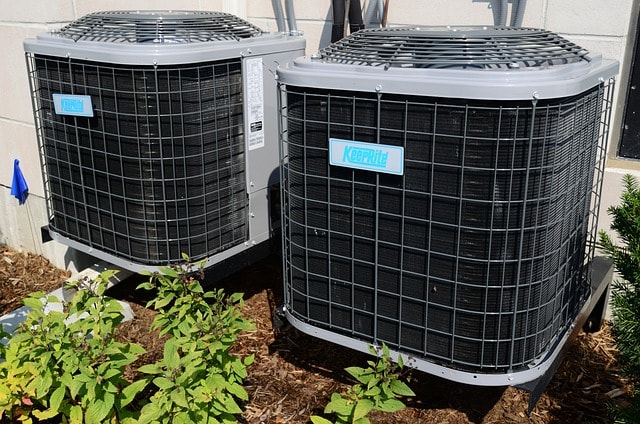

Types of HVAC Systems
Split Systems
Split systems are the most common type of HVAC system, featuring both indoor units and outdoor components. The indoor unit typically contains the evaporator coil and the air handler, while the outdoor unit houses the compressor and condenser coil. These systems are ideal for homes in moderate to hot climates, where efficient cooling is a priority. They are also effective in providing heating during milder winters, with cooled air being circulated through air ducts.
Hybrid Heat Split Systems
Hybrid heat split systems are similar to traditional split systems but with an added energy-saving feature: the ability to switch between an electric furnace and fossil fuels, such as natural gas or oil. This system is ideal for regions with fluctuating temperatures, as it allows homeowners to choose the most efficient energy source based on the weather conditions. In colder climates, hybrid systems provide the flexibility to use gas power for heating during extreme cold while relying on electricity when temperatures are milder.
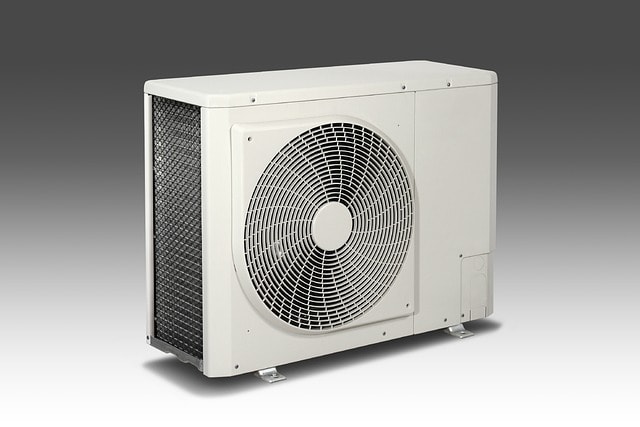

Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Ductless mini-split systems offer a flexible solution for homes without existing ductwork. These systems consist of an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor air handling units, connected by a conduit. They are particularly suited for both hot and cold climates, providing efficient heating and cooling without the need for extensive ductwork. Additionally, duct-free systems allow for zoned heating and cooling, making them an excellent choice for homes with varying desired temperature needs in different rooms.
Packaged Heating and Air Systems
Packaged heating and air systems combine all key components into a single unit, typically installed outside the home. These systems are often used in homes with limited indoor space or in regions where space efficiency is a priority. Packaged systems are versatile, offering both heating and cooling in one compact unit, making them suitable for climates with moderate temperature variations. In commercial buildings and small commercial buildings, packaged HVAC systems are commonly used due to their space-saving design and ability to provide reliable heating and cooling in a single, integrated unit. These systems are also equipped with heat exchangers that efficiently transfer heat, whether for warming indoor spaces during winter or cooling them in summer.
Geothermal HVAC Systems
Geothermal systems harness the stable temperatures beneath the earth’s surface to provide efficient heating and cooling year-round. These systems are environmentally friendly and can significantly reduce energy consumption over time. Geothermal systems are particularly effective in climates with stable ground temperatures, making them a great choice for areas with extreme seasonal variations.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are versatile systems that provide both heating and cooling by transferring heat between the indoors and outdoors. In warmer weather, they work as air conditioning systems, and in colder weather, they reverse the process to provide heat. Heat pumps are ideal for mild to moderate climates, where the temperature does not frequently drop below freezing. They are known for their energy efficiency, particularly in regions with milder winters.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an HVAC System
Climate Compatibility
The first step in selecting the right HVAC system is understanding your climate’s specific needs. For instance, homes in hot climates require systems with strong cooling capabilities, while those in cold climates need efficient heating solutions. Matching the system’s features to your climate ensures year-round comfort and efficiency.

Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical factor to consider, as it directly impacts your utility bills and environmental footprint. Different systems have varying efficiency ratings, such as the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) for heating. Choosing a system with high energy efficiency can lead to significant savings, especially in climates with extreme temperatures.
Additionally, focusing on energy conservation practices, such as regular maintenance and smart thermostat usage, can further enhance the system’s efficiency and reduce overall energy consumption. Moreover, investing in systems that utilize variable refrigerant flow (VRF) technology can offer superior energy management by adjusting the flow of refrigerant according to the needs of different zones in your home, enhancing comfort while minimizing waste.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
While initial installation costs are important, it’s also essential to consider the long-term maintenance and operational costs of the system. Some systems may have higher upfront costs but offer lower maintenance needs and energy costs over time. Additionally, the wear and tear on the system due to climate conditions should be factored into your decision.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of your HVAC system is another crucial consideration. Systems that use renewable energy sources, such as geothermal or solar, have a lower carbon footprint and can contribute to a more sustainable future. Energy conservation is key in reducing the environmental impact of your HVAC system. Opting for energy-efficient models, properly sizing your system, and maintaining it regularly are all ways to support energy conservation and minimize your system’s environmental footprint. Depending on your climate, some systems may offer better eco-friendly options than others.

Regional Climate Considerations
Hot and Dry Climates
In hot and dry climates, cooling efficiency is the top priority. Cooling split systems and ductless mini-split systems are excellent choices for these regions, as they offer powerful cooling and can be equipped with features like dehumidification to enhance comfort. It’s essential to choose a system that can handle high temperatures without consuming excessive energy.
Cold Climates
For homes in cold climates, heating efficiency is paramount. Hybrid heat split systems, electric furnaces, and geothermal systems are particularly well-suited for these regions, as they provide reliable heating even in extreme cold. Proper insulation and heat retention features are also crucial in these climates to maximize the system’s efficiency.
Humid Climates
In humid climates, controlling moisture levels is just as important as regulating temperature. Heat pumps and split systems with advanced humidity control features are ideal for these regions. These systems help maintain a comfortable indoor environment by reducing humidity, preventing mold growth, and improving overall indoor air quality.
Mild Climates
Mild climates, where temperatures don’t reach extreme highs or lows, require flexible HVAC systems that can provide both heating and cooling as needed. Heat pumps and ductless mini-split systems are excellent choices for these regions, offering energy-efficient solutions for year-round comfort without overloading your utility bills.

Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Choosing the right HVAC system for your climate is essential for maintaining comfort, efficiency, and long-term cost savings. Whether you live in a hot, cold, humid, or mild climate, there is an HVAC system tailored to meet your specific needs.
Final Tips
Before making a final decision, it’s always a good idea to consult with an HVAC professional who can assess your home’s requirements and recommend the best system for your climate. Investing in the right HVAC system not only enhances your comfort but also contributes to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.